Overview of the mechanism for groundwater aeration sound extraction
Sounds captured by the pickup sensor include the sound of groundwater flowing, air hissing sound, sound of the friction of sand and gravel, external noise, etc.
This device reduces various noises by means of the filtering functions that restrict frequencies based on the information on the sound measured, and can extract groundwater aeration sound. The filtering functions can respond to the noise generated at the site flexibly, by setting a combination of low frequencies and high frequencies that is easy to be heard from the 16 types of combinations in total, consisting of 4 stages each of low frequencies and high frequencies.
Also, the device has functions for setting the degree of amplification that are used for amplifying the loudness heard through the headphone when the groundwater aeration sound is small, and performs typical value (D) calculation processing for displaying/recording the typical value (D) by quantifying the intensity of groundwater aeration sound.。
On filters
The filters remove the frequency components that are unnecessary sounds (noises), and extract the frequency components of the sound of groundwater flowing.
By performing this processing, it becomes easier to hear the groundwater aeration sound.
This device is provided with the following 2 types of filters.
- Low cut filter
- High cut filter
If the filters are provided, the sounds of the frequency bands below the value set with the low cut filter and above the value set with the high cut filter attenuate, and so it becomes easier to hear the sounds of the frequency band between the low cut filter and high cut filter.
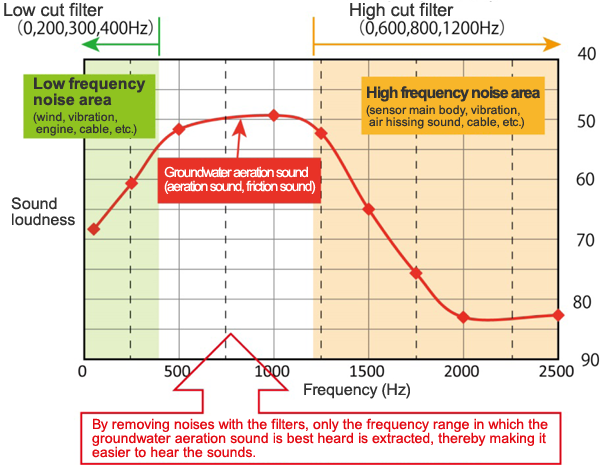
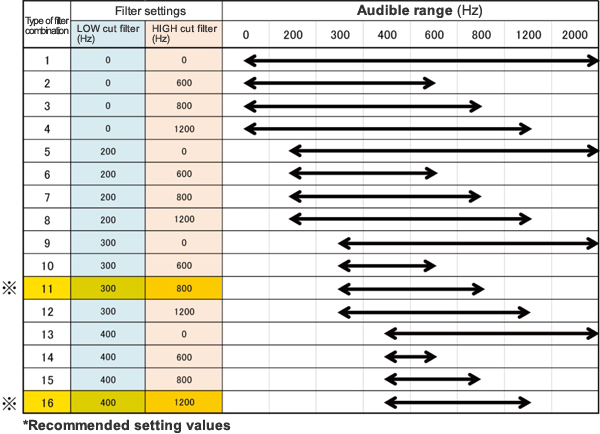
In the filters of this device, it is possible to set the frequency bands in which groundwater aeration sound can be heard easily, by selecting one from those of the low cut filter and by selecting one from those of the high cut filter, and as if the band is gradually narrowed from the entire frequency band, as shown below (Table 1).
- Low cut filer: 4 types; 0 Hz, 200 Hz, 300 Hz, and 400Hz
- High cut filter: 4 types; 0 Hz, 600 Hz, 800 Hz, and 1200 Hz
From the results in the past, the main range of groundwater aeration sound is roughly between 200 Hz and 1500 Hz.
The filters have functions that reduce noise and make the groundwater aeration sound easier to be distinguished by listening to it, and they cannot be eliminate noise completely.
Setting of the degree of amplification
On occasions such as those in which the loudness of the sound heard through the headphone is small, the setting value for the degree of amplification is changed to make adjustment to the loudness that is easier to be heard.
The degree of amplification can be set in 11 steps from 0 to 10, and can be changed by one step at a time.
AMP settings and ratio of amplification
The ratio of amplification for the setting value of each AMP when the signal from the pickup sensor is used as the standard (=1) becomes as shown in Table 2.
Also, the ratio of amplification for the setting value of each AMP when AMP 5 is used as the standard (=1) which is the standard setting, is as shown in the column on the right of the table.
| AMP settings | Ratio of amplification when the pickup sensor signal is used as the standard (=1) (times) |
Ratio of amplification when AMP 5 is used as the standard (times) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 100.8 | 0.225 |
| 2 | 190.4 | 0.425 |
| 3 | 280.0 | 0.625 |
| 4 | 358.4 | 0.800 |
| 5 | 448.0 | 1.000 |
| 6 | 537.6 | 1.199 |
| 7 | 649.6 | 1.450 |
| 8 | 772.8 | 1.725 |
| 9 | 929.6 | 2.075 |
| 10 | 1120.0 | 2.500 |
Typical value (D) calculation processing
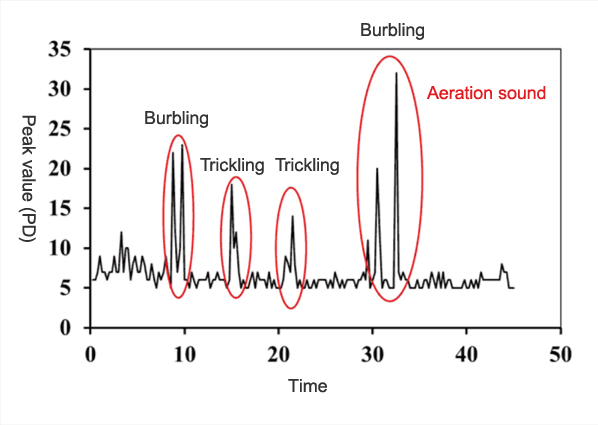
Fig. 2 shows the waveform after processing the groundwater aeration sound. When the bubbling sound of groundwater aeration sound is given off, a peak appears as shown in Fig. 2. In the typical value (D) calculation processing, many of the peak values of this bubbling sound are collected and their average value (typical value (D)) is obtained.
In the calculation processing, processing in 2 steps is performed: primary processing and secondary processing.
By means of this, anyone can obtain the typical value (D) of groundwater aeration sound with the same accuracy by means of correct measurement.