Equipment configuration
[Overview]
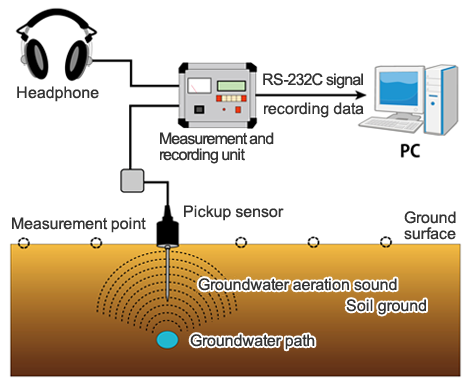
This device consists of (1) a pickup sensor, (2) a measurement recording unit, and (3) a headphone (Photo 1).
The groundwater aeration sound captured by the pickup sensor is processed by the measurement recording unit, and the intensity of the sound can be judged audibly and visually by means of the headphone or a level meter.
The device calculates and displays a typical value of the intensity of groundwater aeration sound at the point of measurement, and at the same time this typical value can be stored in internal memory.
The typical value thus stored can be output to a personal computer by means of RS-232C signals after completion of the measurement, and can be checked by using spreadsheet calculation software, etc. (Fig. 1)
The original sound thus measured includes the external noises such as the sound of groundwater flowing, sound of the wind, frictional sound of sand gravel, etc. The measurement recording unit of this device enables the desired sound to be picked out by reducing various noises other than the groundwater sound by using functions (filters) that restrict the frequencies from the measured source of sound.
The frequency restriction functions enable the noises generated at the site to be dealt with flexibly by setting 4 stages each for the low frequencies and high frequencies and by choosing an easy-to-be-heard combination from 16 types of combinations.


Explanations of various parts
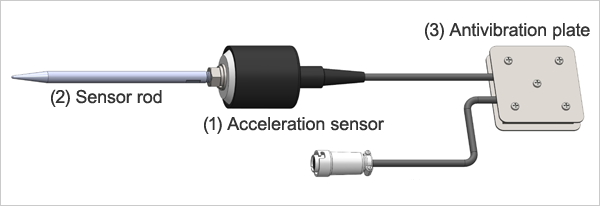
Pickup sensor
The pickup sensor captures weak groundwater aeration sound.
The pickup sensor consists of (1) an acceleration sensor, (2) a sensor rod, and (3) an antivibration plate (Fig. 2).
- (1) Acceleration sensor
The sensor detects weak vibration (sound) that propagates underground at the bottom, and after converting it into a voltage signal, transmits the signal to the measurement recording unit. - (2) Sensor rod
It is an attachment for fixing the sensor to the ground by inserting it into the ground.
(It is intended for fixation of the sensor to the soil ground, and is not a sound detector.) - (3) Antivibration plate
It prevents noise caused by a swaying of the cable or by vibration from being transmitted to the sensor.
Types of fixation tools and how to use them
- 1. Sensor rod (for ordinary soil ground)
A sensor rod is used when fixing a sensor to soil ground where the sensor rod can be inserted (Photo 2).
It is available in 3 lengths: 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm, and is used by changing the length according to the nature of the soil ground where measurement is to be made.20 cm: For soft soil ground where contact of the sensor bottom cannot be maintained.
15 cm: Standard; for ordinary soil ground10 cm: For a place with a shallow soil layer in the soil ground (spraying works on a slope, etc.)

Photo 2 Sensor rod - 2. Sensor disc (for hard soil ground) * To be available for sale shortly (now being prototyped) (an optional tool)
It is used for fixing the pickup sensor to concrete or asphalt where the sensor rod cannot be inserted (Photo 3).

Photo 3 Sensor disc
Accessories* To be available for sale shortly (now being prototyped)
- 1. Windshield
At the time of strong wind, and the like, air hissing sound becomes noise. The air hissing sound is reduced by fitting the windshield to the pickup sensor (Photo 4).

Photo 4 Windshield - 2. Pickup sensor holder
By putting the pickup sensor into the sensor holder, the sensor can be carried safely even on an insecure foothold (Photo 5).

Photo 5 Pickup sensor holder
Measurement recording unit
The measurement recording unit calculates the typical value of groundwater aeration sound by means of a frequency filter that reduces the noise components of the groundwater aeration sound, settings for the degree of amplification (sound loudness), and digital processing, and records the data in its internal memory.
The data thus recorded in the internal memory can be output to a personal computer to be provided separately.
Also, the groundwater aeration sound that has been captured in the frequency band and the degree of amplification (sound loudness) of the frequency filter that have been set is output to the headphone and LINE OUT (Photo 6).
Front view
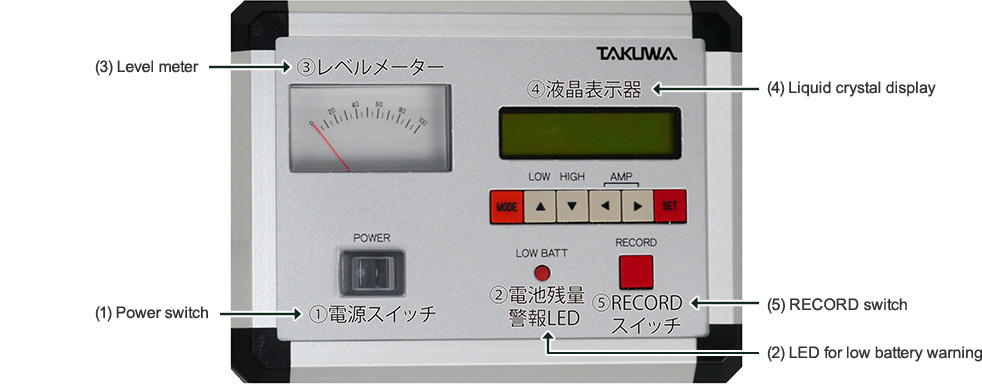
- (1) Power switch
Power is turned off at the "◯" position, and turned on at the "┃" position.
(OFF) ◯
 ┃ (ON)
┃ (ON) - (2) Low battery warning lamp
This unit works on 8 AA batteries (12 VDC).
The low battery warning lamp is lit when the total voltage of the batteries reaches 9 V or below.
When this lamp has been lit, replace the batteries with new ones.
(The batteries can be used for about 15 hours under the conditions of continuous use without turning on the back light.) - (3) Level meter
It is an analog meter for indicating the level of groundwater aeration sound.
The intensity of sound can be grasped visually with the deflection width of the indicator. - (4) Liquid crystal display
It displays the conditions of measurement of groundwater aeration sound, measured data, a clock, various types of settings, etc.
The back light can be turned on during measurement at night. - (5) Operation switches
They are switches for performing various types of operations, such as a switching of the display, changes in the setting values, etc.
There are 6 switches: MODE, ▲, ▼, ◀, ▶, and SET. - (6) RECORD switch
It is a switch for starting the recording of measured data. It also is used for erasure of recorded data.
Side views
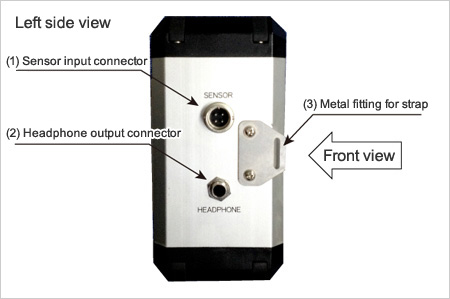
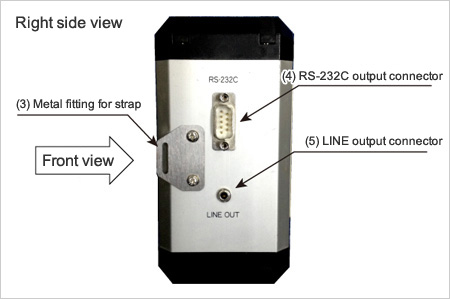
- (1) Sensor input connector
It is a connector for connecting the pickup sensor. - (2) Headphone output connector
It is a connector for connecting the headphone. - (3) Metal fitting for strap
It is a metal fitting for installing the strap that is included as an accessory. - (4) RS-232C output connector
It is an RS-232C connector for outputting recorded data to a personal computer (PC) or the like. - (5) LINE output connector
It is a connector for outputting the waveform signals of groundwater aeration sound of the frequency band and the degree of amplification that have been set.
The connection is made with a stereo mini jack of 3.5 mm in diameter.
By connecting an external measuring device, voice recorder, or the like, the groundwater aeration sound can be recorded, and also by connecting a headphone, speaker, or the like, those other than the person making the measurement can also listen to the sound at the same time.
Headphone
The groundwater aeration sound that has been captured with the pickup sensor and has been frequency filter processed and processed for amplification by means of the measurement recording unit can be listened to on a real time basis.
It is a headphone of the tightly closed type having good sound reproducibility that enables the sound to be distinguished easily (Photo 8).


