Grasping the outline of landform
In order to determine the areas for the measurement of groundwater aeration sound, it is important to grasp the features of landform where a collapse is likely to occur (groundwater is likely to concentrate).
- Prepare landform maps (Geospatial Information Authority of Japan 1:25000 scale landform maps, shaded maps, etc.), aerial photos, etc.
- Grasp the outline of landform at the site.
< Point > Groundwater is likely to flow in a place having a gap in terms of water permeability from its surrounding areas such as a fault, joint, side cliff in landslide landform, tongue area, geological boundary, crack, shattered zone, etc. Also, on a dent or knick point in a slope, spring water is likely to occur. It should be grasped whether there is any such geological structure at the site beforehand by means of aerial photos, landform maps, CS stereoscopic maps, etc. By making a CS stereoscopic map, it becomes easier to understand which are the places where water is likely to exist.
Reference literature:
· Nagano Prefectural Government > Nagano Prefectural Government Forestry Comprehensive Center > Research Results > Propagation of/education on results > Method of creating "microlandform maps" by using numerical landform data
https://www.pref.nagano.lg.jp/ringyosogo/seika/documents/bichikei.pdf
· Edited by the Forest-road Network Subcommittee Experts Meeting (2014) "Techniques for Studying Forest-road Network Arrangements in a Cat Forest-road Network within a Forest Using the 'Stereoscopic Landform Chart of the Nagano Prefectural Government Type = CS Stereoscopic Chart.'":
Nagano Prefectural Government; Forest-road Network Subcommittee of the Nagano Prefectural Government Forestry Improvement Acceleration and Revitalization Conference
http://www.rincon.or.jp/sinrinseibikasokukaringyosaiseikyogikai/ - At the time of site survey, the measurement line is determined so that information on the site such as that described above will not be overlooked.
Determination of the measurement line
By taking account of the features of landform in which collapse is likely to occur, the measurement line and measurement intervals are determined.
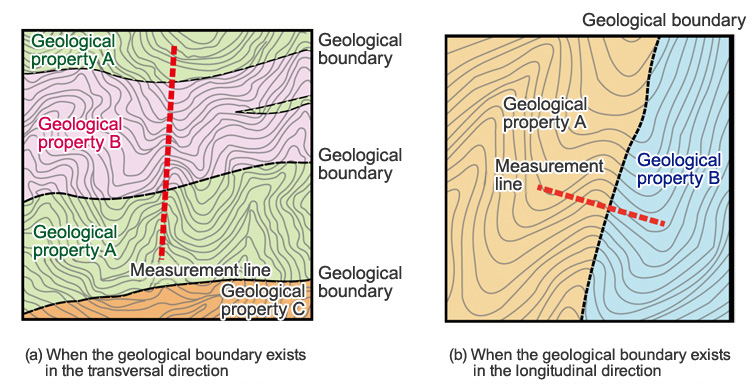
In the case of a landform made up of geological properties of the horizontally deposited structure, by providing a measurement line in the longitudinal direction, it becomes easier to find a geological boundary where spring water is likely to occur (Fig. 1(a)).
A place where spring water is likely to occur resulting from a fault in the longitudinal direction or geological boundary, etc. becomes easier to find by providing a measurement line in the transversal direction (Fig. 1(b)).
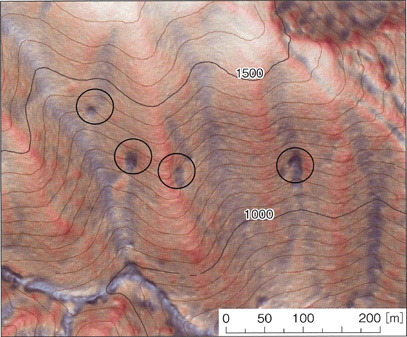
The intervals of measurement should be such that no groundwater path will be overlooked, and it is considered that, in particular, small dented landforms that are found on the ground surface on a slope were formed by erosion due to spring water in the past (Fig. 2; Photo 1), and therefore measurement of such landforms must be made without fail.
 (Reference literature: Edited by Shin Nihon Henshu Kikaku (2014) "Techniques for Slope Collapse Preventive Measures: Mechanism, Sensing, Monitoring System and New Method of Construction Work" P. 229, NTS Inc.) |

(Reference literature: Edited by the Forest-road Network Subcommittee Experts Meeting (2014) "Techniques for Studying Forest-road Network Arrangements in a Forest-road Network by Using the 'Stereoscopic Landform Chart of the Nagano Prefectural Government Type = CS Stereoscopic Chart''' p.16: Nagano Prefectural Government; Forest-road Network Subcommittee of the Nagano Prefectural Government Forestry Improvement Acceleration and Revitalization Conference) |
